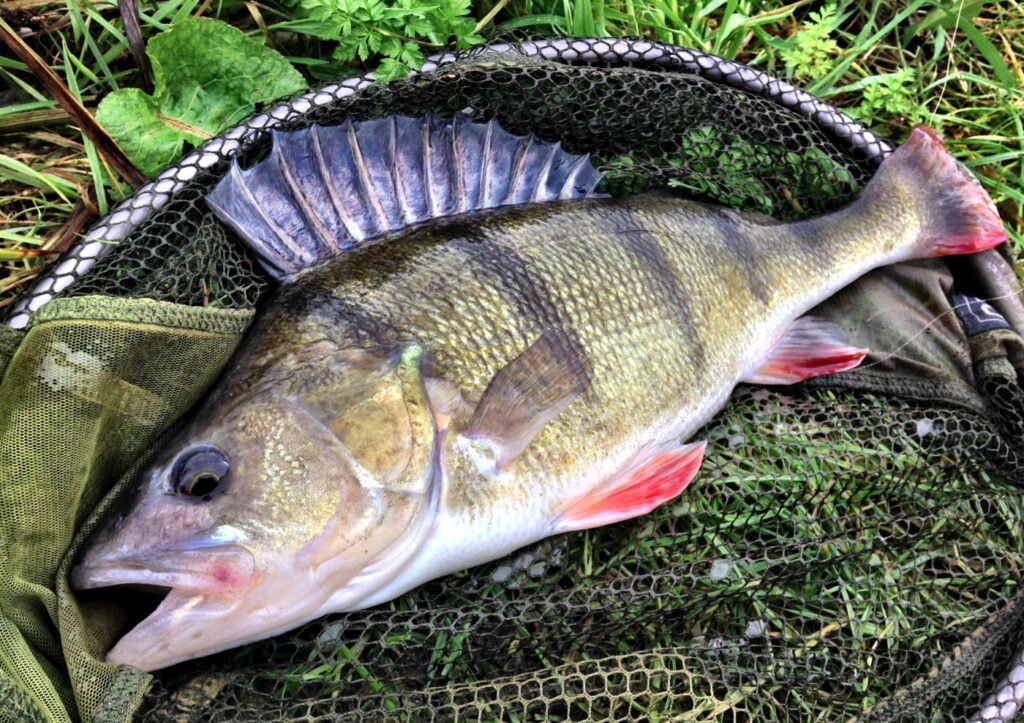
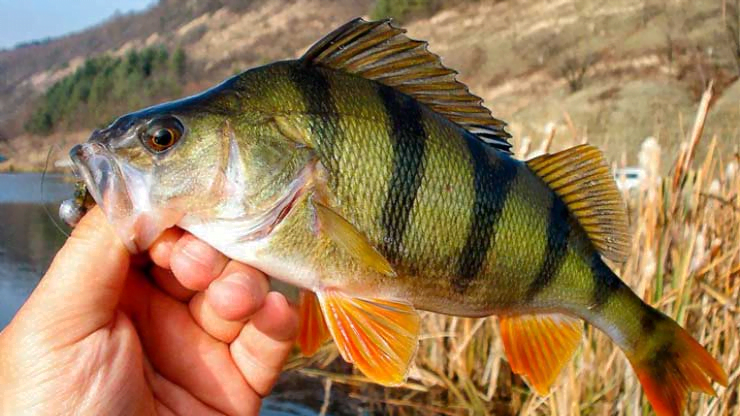
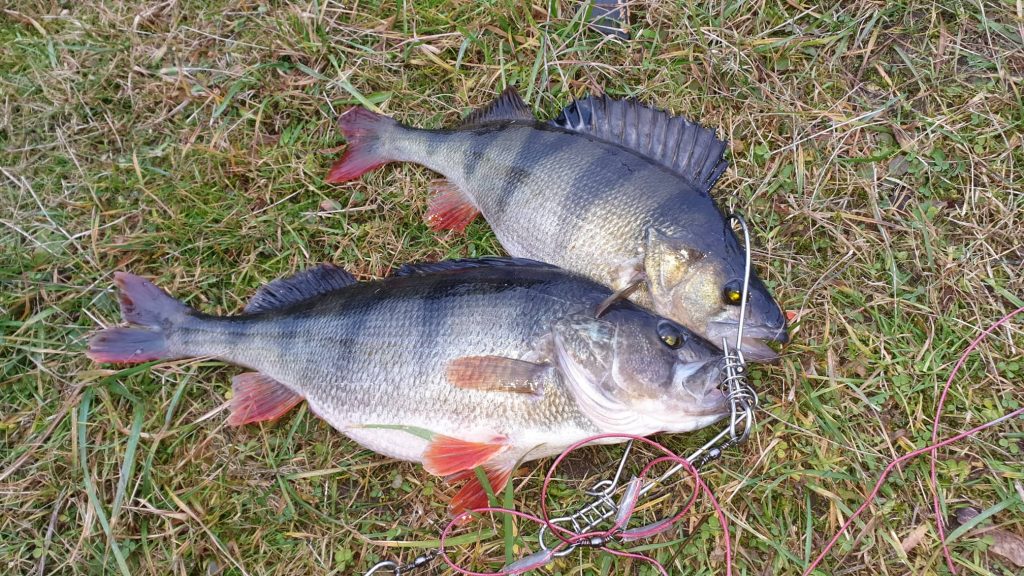
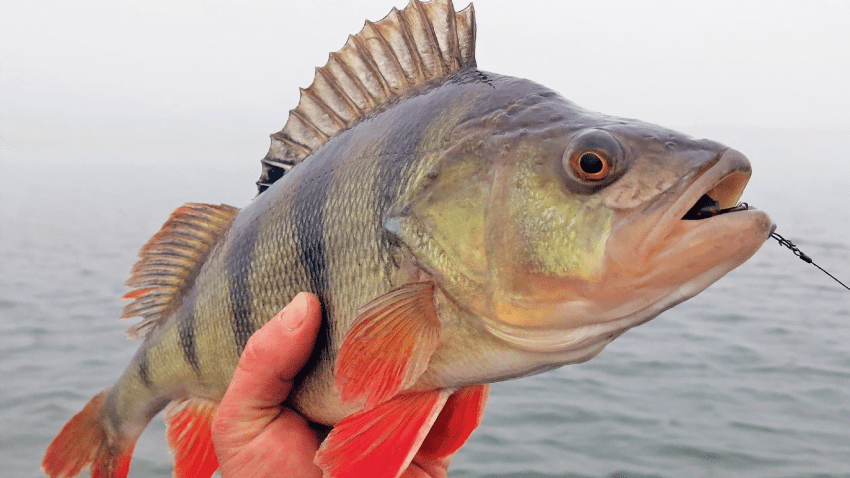
Ešerys – viena iš labiausiai paplitusių žuvų mūsų šalyje. Ešerių galima rasti visur: upėse, ežeruose, tvenkiniuose ir rezervuaruose. Ešerius galima gaudyti žiemą, vasarą, pavasarį… Juos galima žvejoti spiningu, plūdine, ant gyvo mailiaus, avižėle ir t.t.. Pamėginkime šią gražią žuvį pažinti iš arčiau.
Kaip atrodo ešerys
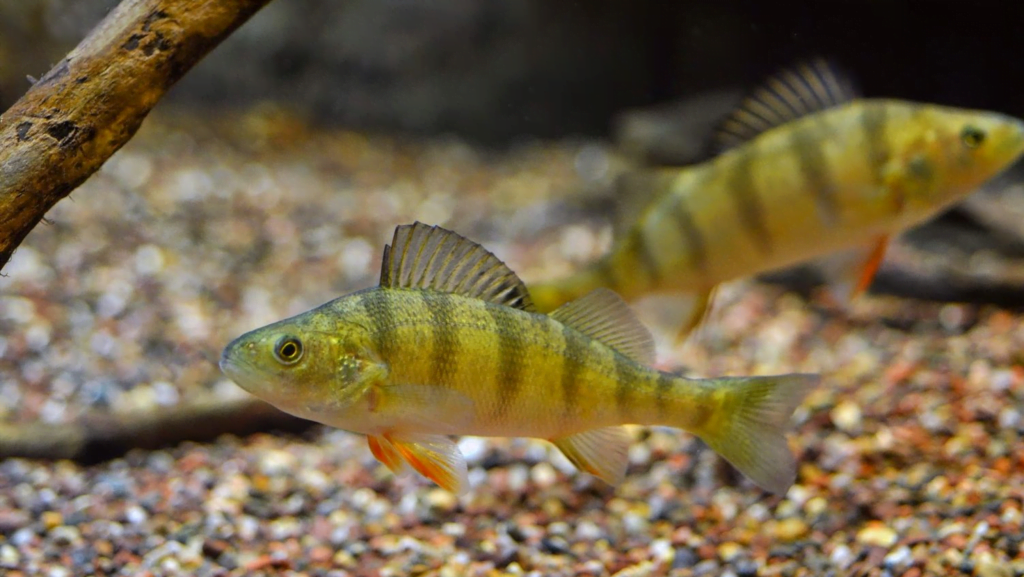
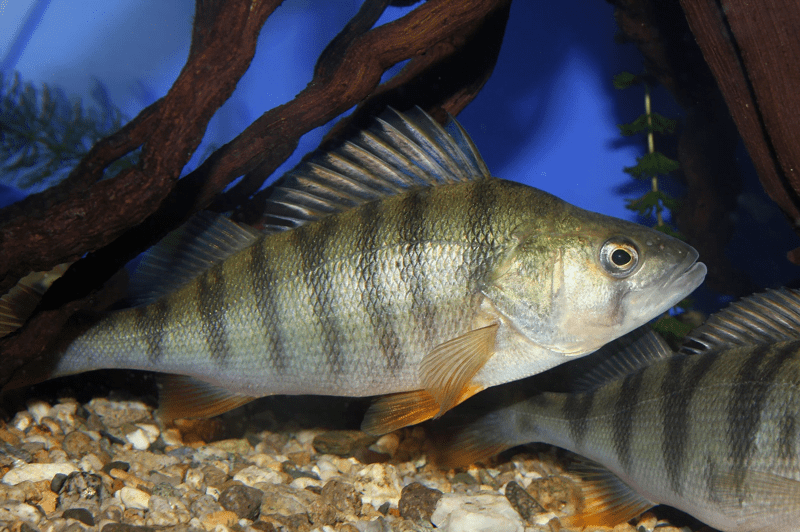
Dėl įspūdingos išvaizdos ir ryškių dryžių spalvos ešerį sunku supainioti su kitų rūšių žuvimis. Ešerys turi iš šonų suspaustą kūną, padengtą tankiais smulkiais žvyneliais. Ešerio kūno aukštis yra trečdalis jo ilgio, todėl ešerys atrodo kaip masyvi žuvis.
Ešerio nugara tamsi, žalsvos spalvos. Ešerio šonai žalsvai gelsvi su tamsiais skersiniais dryžiais. Tamsių juostelių skaičius gali būti nuo 5 iki 9 vienetų. Jaunų ešerių skersinių juostelių spalva šviesesnė, vyresnių – tamsesnė. Ešerio pilvas šviesus, baltai gelsvo atspalvio. Dideli ešeriai turi aiškiai išreikštą kuprą ant nugaros.
Ešerys turi du nugaros pelekus, esančius arti vienas kito. Pirmasis nugaros pelekas yra aukštesnis ir ilgesnis už antrąjį, yra pilkai žalios spalvos, ant jo yra juoda dėmė, kuri yra išskirtinis rūšies bruožas. Pirmąjį nugaros peleką sudaro 12–16 kaulinių ataugų, kurie visi yra kieti ir aštrūs. Antrasis nugaros pelekas yra geltonai žalios spalvos, susideda iš 12-17 ataugų.
Ešerių krūtinės pelekai geltoni, kartais net raudoni. Analiniai pelekai oranžiniai arba raudonai geltoni, susidedantys iš 8-10 ataugų. Uodeginis pelekas prie pagrindo tamsus, o šonuose ir gale – raudonas.
Ešerio spalva labai priklauso nuo jo buveinės, vandens skaidrumo, dugno spalvos. Ešeriai, gyvenantys rezervuaruose su skaidriu vandeniu ir smėlingu dugnu, yra šviesesnės kūno spalvos nei tie, kurie gyvena tamsiuose durpynuose ežeruose su dumblinu dugnu.
Ešerio galva yra vidutinio dydžio, su šeriniais dantimis burnoje, kurie yra keliomis eilėmis gomuryje ir ant žandikaulių. Šeriniai dantys nesuteikia ešerių grobiui galimybės ištrūkti iš burnos. Ešeris neturi ilčių. Ant ešerio žiaunų gaubtų – aštrūs spygliai, apsaugantys jį nuo plėšrūnų, bent kartą pagavusieji ešerį žino, kokie jie aštrūs ir kokius gilius įpjovimus palieka ant rankų. Ešerio akys didelės, rainelė geltona.
Išoriškai ešerių patinai praktiškai nesiskiria nuo patelių, išskyrus prieš neršto laikotarpį, kai patelių pilvas prisipildo ikrais.
Kiek ešeriai gyvena ir kokie užauga
Maksimalus ešerių dydis kiekviename vandens telkinyje labai skiriasi. Pasitaikė atvejų, kai net gretimuose tvenkiniuose gyvenančių ešerių maksimalus dydis labai skiriasi.
Ešerių gyvenimo trukmė ir dydis priklauso nuo konkretaus rezervuaro. Dideliuose vandens telkiniuose tikimybė sugauti stambius, trofėjinius ešerius yra daug didesnė.
Vidutinis suaugusio ešerio dydis yra 15-20 cm. Paprastai ešerio ilgis neviršija 50 cm, o svoris – 2 kg.
Maksimali užfiksuota ešerio gyvenimo trukmė yra 23 metai. Tokio amžiaus ešerys buvo sugautas Khubsugul ežere Mongolijoje, jo ilgis siekė 44,7 cm, o svoris – daugiau nei 2 kg.
Ešerio gyvenimo būdas
Ešeriai gyvena upėse, ežeruose, tvenkiniuose ir rezervuaruose, bet aptinkami ir Alpių ežeruose, iki 1000 metrų virš jūros lygio.
Ešeriai gali gyventi sūriame vandenyje, aptinkami Baltijos ir Kaspijos jūrų pakrantėse.
Ešerys yra plačiai paplitusi žuvis ir randama daugumoje vandenų. Kai kuriuose vandenyse ešeriai gali būti vienintelė jame gyvenanti žuvis.
Rezervuaruose ešeriai laikosi prie vandens augalija apaugusios rezervuaro pakrantės zonos, taip pat rezervuarų atkarpų su dirbtinėmis ir natūraliomis pastogėmis.
Didžiąją savo gyvenimo dalį ešeriai praleidžia prie dugno. Dideliuose rezervuaruose dideliame gylyje mažų ešerių pulkai yra gelmių šlaituose, tai yra vietose, kur smarkiai padidėja gylis. Ešerių pulkai eina į sėklius medžioti mailiaus, kurių tokiose vietose būna daug.
Ešeriai nemėgsta šalto vandens ir sraunių srovių, jo nerasite šaltose upėse. Daugumoje vandens telkinių ešeriai laikosi vietose, kur vandens temperatūra yra nuo 13 iki 19 laipsnių.
Ešerių katilas atsiranda, kai ešerių pulkas apsupa mailių, priversdamas mailių pakilti į patį paviršių ar net iššokti iš vandens, bandydamas pabėgti nuo godžių plėšrūnų. Vanduo tokiose vietose, kaip sakoma, užverda.
Ešeriai mėgsta būti prie sugriautų tiltų, prie didelių akmenų. Dėl žalsvos spalvos jie gali puikiai maskuotis tarp vandens augalijos ir užpulti mažas žuvis. Stambūs ešeriai gyvena gilesnėse vietose, duobėse.
Maži ešeriai medžioja būriais, dideli ešeriai – vieni. Ešeriai aktyviai persekioja grobį, šokinėja į vandens paviršių, kartais net į krantą. Medžioklės metu ešeriai išskleidžia nugaros peleką. Dideli ešeriai medžioja iš pasalų kaip lydekos.
Ešeriai laikosi prieblandos gyvenimo būdo, medžioja šviesiu paros metu, o aktyvumo pikas yra ties dienos ir nakties riba, tai yra ryto ir vakaro prieblandoje. Naktį ešerių aktyvumas smarkiai sumažėja.
Rudenį ešeriai telkiasi į didelius pulkus ir apsistoja gilesnėse ir atviresnėse vietose. Šaltuoju metų laiku ešeriai lieka prisispaudę prie dugno. Kuo didesnis ešerys, tuo gilesnėse vietose jis laikosi. Žiemą ešeriai, kaip ir vasarą, yra aktyvūs dienos metu, aktyvumas padidėja sutemus ir nėra aktyvus naktį.
Kaip ešeriai dauginasi
Ešerių nerštas, kaip taisyklė, įvyksta iškart po lydekų neršto. Didieji ešeriai pradeda neršti vėliau nei maži.
Patinai neršti pasiruošę 2-3 metų amžiaus, patelės kiek vėliau, 4-5 metų amžiaus. Išvaizdos pokyčių neršto metu ešeriuose nebūna. Nerštas paprastai trunka 4-5 dienas. Ešerio patelės vaisingumas yra nuo 12 000 iki 300 000 kiaušinėlių, priklausomai nuo jos dydžio. Patelę neršto metu lydi keli patinai.
Neršto metu patelė deda tinklinius želatininės medžiagos kaspinus ant pernykštės augmenijos, užlietų krūmų ar net tiesiog ant dugno, o patinai juos apvaisina. Ešerių kiaušinėlių skersmuo apie 4 mm, juostelės ilgis mažiems ešeriams gali būti nuo 12 cm, dideliems iki 1 metro.
Praėjus maždaug dviem savaitėms po neršto, iš jo išsirita apie 6 mm ilgio ešerių lervos. Išsiritusios ešerių lervos minta vėžiagyvių lervomis ir kitais smulkiais vandens organizmais. Netrukus ešerių lervos persikelia į gilesnę rezervuaro zoną, kur minta zoo planktonu ir lieka viršutiniuose vandens sluoksniuose. Po trijų keturių savaičių užaugusios ešerių lervos vėl grįžta į pakrantės zoną.
Kai kūno ilgis yra 15-20 mm, ešerio lerva tampa mailiumi, o kai kūno ilgis 20-25 mm ant mailiaus pastebimos tamsios ešerio juostelės.
Kuo minta ešerys
Pirmaisiais gyvenimo metais ešeriai minta zooplanktonu ir kitais smulkiais vandens organizmais. Kai tik ešerys pasiekia 4 cm ilgį, kas dažniausiai būna antraisiais gyvenimo metais, o kartais ir pirmaisiais, jis pradeda maitintis mailiumi.
Žuvis pagrindiniu ešerio maistu tampa tik pasiekus 15 cm ilgį, tačiau net ir dideli ešeriai toliau minta ne tik žuvimis, bet ir zooplanktonu ir kitu gyvūniniu maistu.
Didėjant ešerio amžiui, jis pradeda medžioti vis didesnius ir greitesnius objektus. 3 metų ešerys minta 2–4 cm dydžio žuvimis, 6 metų – 2–8 cm dydžio žuvimis.
Ešeriai minta ne tik žuvimi, bet ir kitu gyvūniniu maistu. Ešerių mityba priklauso nuo rezervuaro, kuriame jis gyvena, taip pat gali skirtis priklausomai nuo metų laiko ir maisto prieinamumo. Ešeriai lengvai pereina nuo vieno maisto prie kito.
Ešeriai mieliau minta siaurakūnėmis žuvų rūšimis pvz. kuoja. Be žuvų, ešeriai minta vabzdžių lervomis, varlėmis, vėžiais.
Ešeriai yra linkę į kanibalizmą, stambesni ešeriai valgo savo mažesnius gentainius. Dažniausiai tai nutinka arba vėlyvą rudenį, kai ešerių mailius persikelia į gilesnes vietas, arba vandens telkiniuose, kuriuose daugiausiai gyvena tik ešeriai. Kanibalizmas yra apsauginis mechanizmas, ribojantis nekontroliuojamą ešerių dauginimąsi.
Pavasarį, tirpstant sniegui, ešeriai minta kirmėlėmis ir bestuburiais, kurie kartu su tirpstančiu ledu patenka į vandenį. Vasarą ešeriai minta įvairiausiu gyvuliniu maistu, kuriame didelę dalį sudaro mailius. Ešeriai ypač aktyviai maitinasi rudenį, o tai susiję su pasiruošimu žiemai. Būtent rudenį ešerių dydis ir svoris labiausiai padidėja.
Ešerys toks godus, kad taip prisikemša pilvą, kad sugautos žuvies uodegos, kurios netelpa į skrandį, gali išlįsti iš burnos. Dešimt mėnesių per metus ešeriai ryja viską, kas juda ir primena maistą.
Ešerys kulinarijoje
Ešerių mėsa turi gerą skonį. Palyginti su kitomis žuvimis ešeriai turi nedaug kaulų. Ešerio mėsa laikoma dietiniu produktu, 100 gramų yra tik 82 kcal. Ešerio mėsa savo skonį išlaiko net ir užšaldžius 3-4 mėnesius.
Iš ešerių verdama nuostabi žuvienė, ruošiami žuvies konservai ir filė, ešeriai kepami, džiovinami, kepami, rūkomi.
Įvairūs ešerių patiekalai labai populiarūs Skandinavijos ir Rytų Europos šalyse. Suomijoje iš ešerių gaminamas nacionalinis patiekalas kalakukko – ešerių pyragas su lašiniais. Italijoje ešeriai baltame vyne laikomi Kalėdų patiekalu.
Karštas rūkymas yra vienas geriausių ešerių paruošimo būdų. Ešerių rūkymui geriausia naudoti alksnio, uosio, obels ar vyšnių drožles.
Yra daugybė paruošimo receptų. Išbandykite įvairius ešerių receptus, eksperimentuokite ir nenusivilsite.