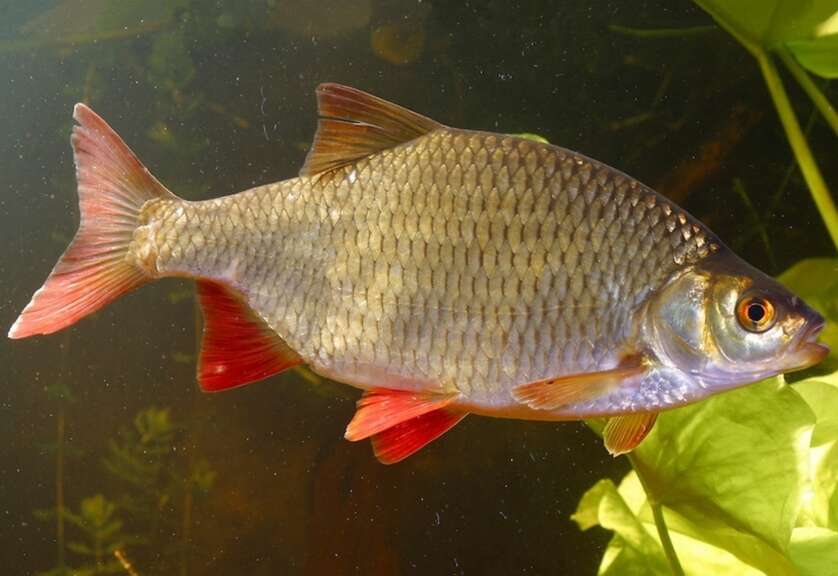
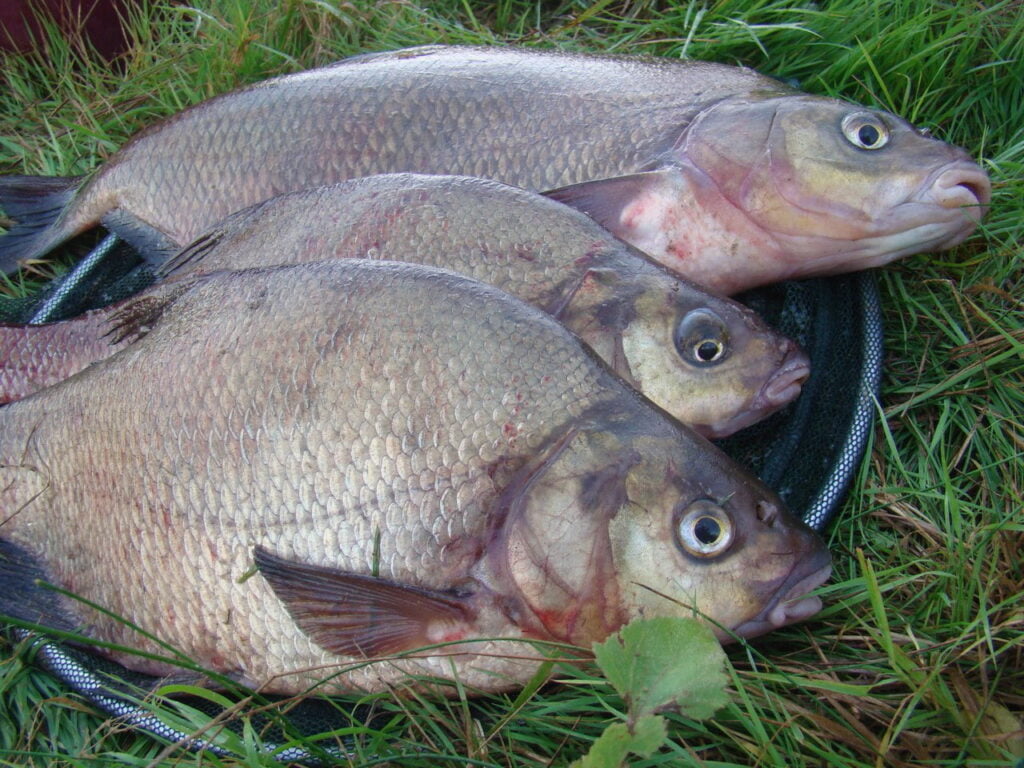
Whitefish is a wonderful fish that belongs to the carp family. Plakis lives in large groups. Everyone knows about this small fish, even young fishermen, unfortunately, it is not possible to catch it everywhere. It is also unlikely that you will be able to catch large specimens, so this article will be devoted to familiarization with the whip.
What does a whip look like?
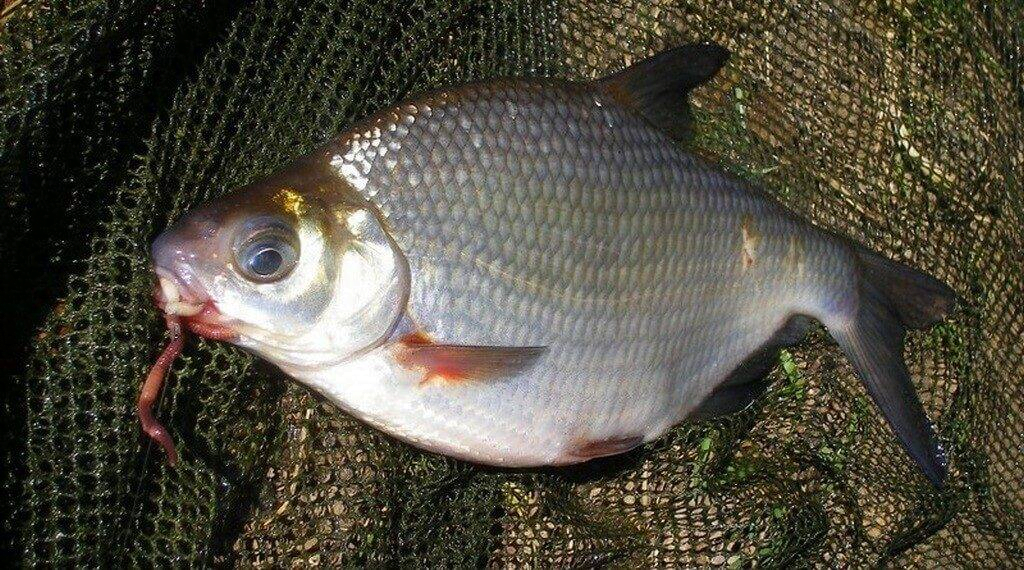
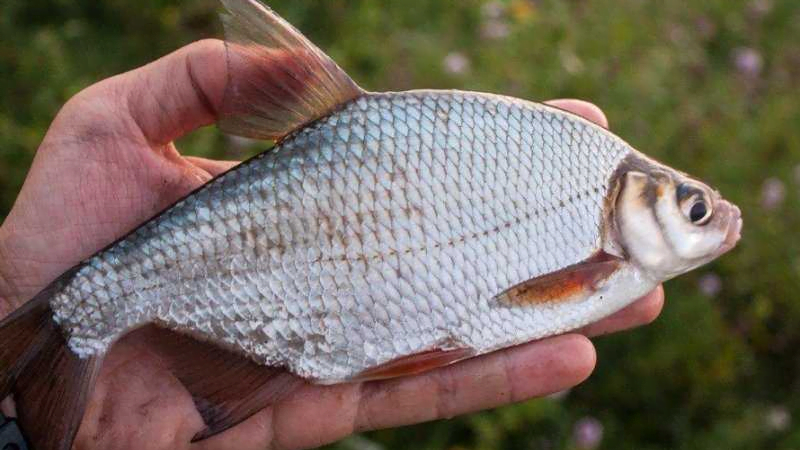
The look is very reminiscent of a whip bream. The body is also flattened laterally and is very bony. However, many anglers still prefer to fry, smoke or dry the whip.
It is worth noting that this fish has 7 teeth on each side. The head ends in a blunt snout, and the lower jaw protrudes slightly forward. The whip has no mustache near the mouth.
Compared to bream, the whips are distinguished by larger scales, and a peculiar groove runs along the head. Another difference from close relative bream is that it has significantly more rays on its fins.
As for the enemies, they are the same as any other white fish:
The whip grows up to 35 cm, and its weight can reach more than 1 kilogram. However, such trophy specimens are quite rare.
Whip lifestyle
Whitefish is considered a lazy fish. Fish prefer to rest on the bottom, among the grass. The sluggish lifestyle of whips is similar to that of bream, so they get along well together. The whip eats differently in different periods of its life. It grows slowly, it grows about 5 centimeters in length per year.
Likes to eat crustaceans, worms and molluscs. Does not miss insects that live near water. Fry look for food on the surface of the water, while adults feed on the bottom. Fish live in one place for a long time. They go on a trip only in spring - to spawn, and in autumn - to hibernate in holes. The woodpecker hibernates in burrows in groups.
A short lifespan is associated with many enemies among predators. This is why fish rarely die of natural causes. Fish are at risk from the moment they stick to the algae as eggs. Due to changes in water levels, many eggs do not develop into fry. A seasonal drop in water level washes the eggs ashore and they dry out. There are also many threats in the water from predators that like to feast on caviar. After the fry appear, the dangers do not decrease. The high reproduction rate does not allow the fish population in water bodies to decrease.
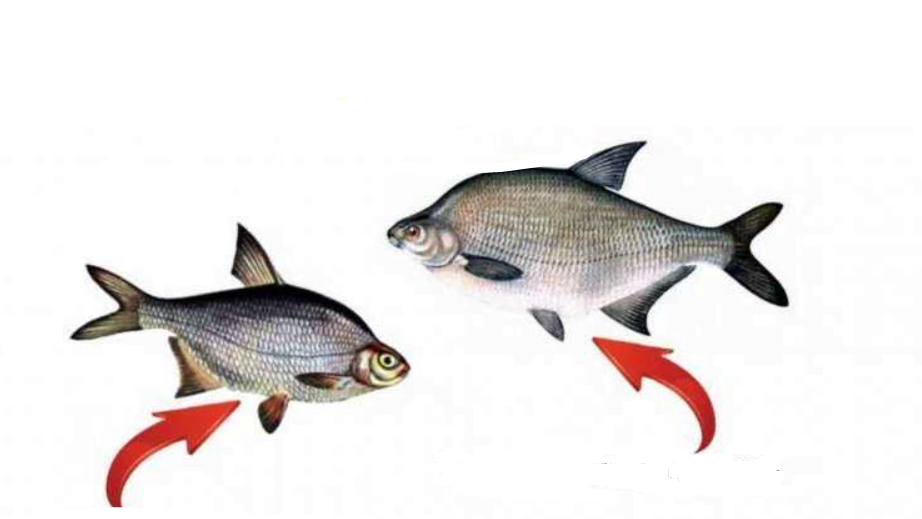
What is the difference between whip and bream
Plakis live next to their closest relatives - bream. Fish are often confused because they have some similarities. Usually, inexperienced fishermen confuse the fish. More experienced anglers know quite a few differences between whiting and bream. The whiting is distinguished by bright silver scales, while the bream has a bronze hue. There is also a difference in size, with whiting having large scales and bream having small scales. The scales have a thick layer of mucus on the scales, but there is none on the whip. Of course, the main difference between the fish is their fins. In bream, they are gray, while whip fins have a pinkish tint. By knowing these differences, the fish will never look the same.
The main differences between bream and whiting:
- The eyes of the rays are smaller.
- The scales of heather are smaller and denser. Its color is not silver, but with a bronze tint.
- The anal fin of plaice consists of 24-29 rays, while that of bream consists of 19-24 rays. ie Karshi's anal fin is smaller.
- A heath's scales are covered with a thick layer of mucus, and its whip is almost free of mucus.
- Stingrays have gray fins, while whitefins have yellow or red fins.
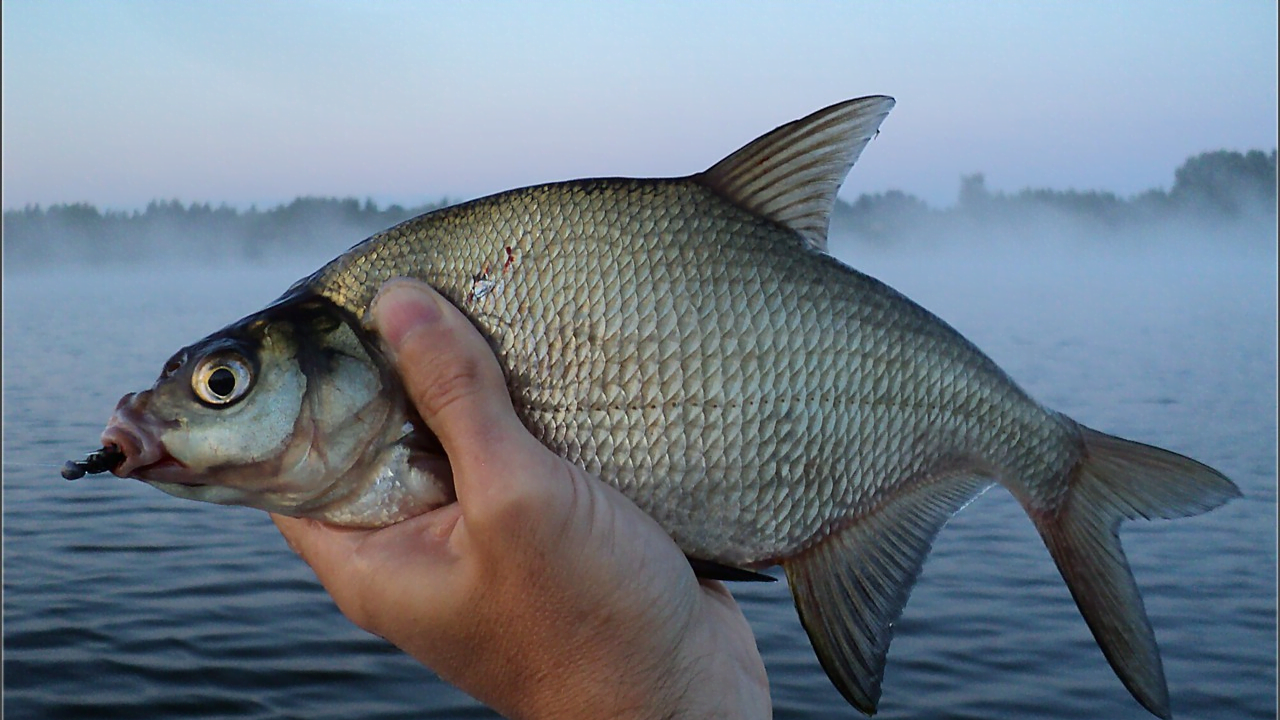
What does the whip eat?
Silver bream do not eat their own kind, neither fry nor fish eggs. Eats both vegetable and protein food. In the natural environment, these are:
- Water larvae
- Crustaceans
- Worms
- Algae and detritus
- Small clams
- Coastal vegetation
- Insects that live near water
To catch this fish, people use bait that is not so natural for the water environment:
- Dzik
- Earthworms
- Matylius
- Dough
- Corn from a can
- boilies

How whips reproduce
Until puberty, whips prefer to stay in one place and do not swim far. This changes after 3 years of life, ready to reproduce. Males are often ready to breed earlier than females. Then mature whiting begin to migrate to the spawning grounds. It is a seasonal phenomenon, starting in April, when the water warms up to 16° - 18°, and ending in July. The fish spend the rest of the summer in the place where a large school has gathered.
Still water for sexual insemination. These can be inlets, bays, shallow bays and straits, flooded grassland areas. The depth there is not very deep, but there are many fish, so there is a loud noise from the splashing water, which gives away the spawning area. The spawning site chosen by whiting does not change and they swim to the same place year after year.
Spawning can take weeks. A large individual can lay more than 100 thousand eggs, smaller ones - from 10 thousand. Caviar matures for up to 10 days, then it hatches into fry. Fry stay closer to shore where they can find zooplankton and algae particles for food. A little later, they start feeding on small crustaceans and molluscs.
Whip in cooking
This type of meat has a lot of bones, which makes it difficult to cook. But the taste is worth the painstaking work, because a well-cooked whip becomes a real delicacy. The vitamin-mineral set is full of various useful elements. Meat contains vitamins A, B, PP, D. It also contains fluorine, iron, chromium, sodium, magnesium, calcium. Eating whip will have a positive effect on the cardiovascular system, nervous system, skin, teeth and even human memory. This is a real treasure for dieters.
This fish is considered dietary, only 96 kcal per 100 grams. This fish, if it is prepared correctly, is very tasty in any form - boiled, stewed, fried, dried, smoked.





